Weight loss: Causes, Symptoms and Diagnosis
Suffering from Unexplained Weight loss? Know all the reasons here.
HEALTH
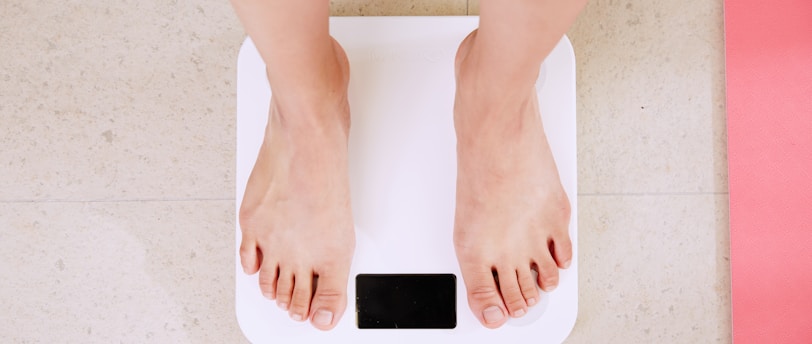

Unexplained weight loss refers to a significant drop in body weight that occurs without intentional efforts like diet, exercise, or lifestyle changes. Losing 10 pounds or more, or five percent of body weight, within 6 to 12 months is considered “unexplained.” This can signal a serious underlying condition or illness, so it's crucial to seek medical attention if you experience such weight loss.
Causes of Unexplained Weight Loss
1. Cancer
Symptoms: Unexplained weight loss often accompanies cancers of the esophagus, stomach, pancreas, and lungs. Ovarian cancer may cause weight loss when a tumor presses on the stomach, causing a feeling of fullness.
Mechanism: Cancer can cause nausea, lack of appetite, and difficulty eating. It also increases inflammation, disrupting hormones that regulate appetite and leading to fat and muscle breakdown.
Diagnosis: Tests like ultrasound, CT scans, tumor marker tests (CEA, CA-125), chest X-rays, upper endoscopy, and biopsy help in diagnosing cancer.
2. Hyperthyroidism
Symptoms: Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much hormone, speeding up metabolism. This can cause weight loss, hand tremors, and a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
Diagnosis: Thyroid function tests (T3, T4, TSH), Anti-TPO antibodies, and iodine uptake scans can confirm hyperthyroidism.
3. Uncontrolled Diabetes
Symptoms: In type 1 diabetes, the body can't use sugar for energy due to lack of insulin, leading to weight loss as sugar is excreted in urine.
Diagnosis: Blood tests like HbA1c and blood sugar levels (fasting and postprandial) are used to diagnose diabetes.
4. Tuberculosis (TB)
Symptoms: TB, an infectious disease affecting the lungs, causes prolonged cough (sometimes with blood), chest pain, weakness, fatigue, weight loss, fever, and night sweats.
Diagnosis: Rapid diagnostic tests like Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra and Truenat assays, along with tuberculin skin tests (TST) or interferon-gamma release assays (IGRA), help detect TB.
5. Chronic Inflammatory Diseases
Chronic inflammation can lead to various conditions, each affecting body weight differently.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Inflammation in joints increases metabolism and muscle wasting, leading to weight loss.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis cause malabsorption of nutrients due to intestinal inflammation.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Inflammation in the lungs increases energy expenditure and muscle wasting.
Lupus (SLE): Inflammation in multiple organs and medication side effects affect metabolism and appetite.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Long-term kidney inflammation leads to protein-energy wasting.
Mechanisms Linking Chronic Inflammation to Weight Loss
Increased Metabolic Rate: Chronic inflammation can increase the body's resting metabolic rate, leading to greater energy expenditure.
Appetite Suppression: Pro-inflammatory cytokines can affect the brain's appetite-regulating centers, reducing hunger.
Muscle Wasting: Inflammation can promote muscle breakdown, leading to loss of muscle mass.
Malabsorption: In conditions like IBD, inflammation can damage the gastrointestinal tract, impairing nutrient absorption.
6. Depression
Symptoms: Depression causes persistent sadness and lack of interest in activities, often leading to unintentional weight loss.
Mechanism: Neurotransmitter imbalances reduce appetite and pleasure from eating, and chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, increasing metabolic rate. Depression also disrupts the gut-brain axis, causing gastrointestinal issues that reduce food intake.
Diagnosis: Scales like the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS) and Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) are used to assess the severity of depression.
Conclusion
Unexplained weight loss can be a symptom of various serious conditions. It's essential to consult a healthcare provider to identify the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. Regular monitoring and timely medical intervention can help manage these conditions effectively.
